
High-resolution views of HIV-1 reverse transcription initiation
Reverse transcription of the HIV-1 viral RNA genome (vRNA) is an integral step in virus replication. A packaged viral enzyme, reverse transcriptase (RT), initiates DNA synthesis at the 3′-end of a host tRNALys3 that is part of a binary complex preassembled with the 5′-end of the vRNA. Reverse transcription is a key target for antivirals, including nucleoside analogs that act as chain terminators and non-nucleoside inhibitors (NNRTIs) that allosterically disrupt enzyme function. While the elongation phase has been characterized in detail by a wide range of structural, biophysical, and biochemical approaches, key structural details of RT initiation and its inhibition have remained unclear. We have studied RT initiation using biochemical and structural methods to define protein-RNA contacts in the initiation complex and characterize the effects of NNRTIs on this process. Our recent high-resolution cryo-EM structures of RT initiation complexes uncovered binding sites for the NNRTIs nevirapine and efavirenz and identified interactions between RT residues and the vRNA template. Our current research focuses on understanding how the vRNA 5′-UTR interacts with the initiation complex and affects the transition to elongation.

Figure 9
Figure 9 Structure of the HIV-1 reverse transcription initiation complex, with reverse transcriptase (RT; grey/blue) bound to viral genomic RNA (yellow) and host tRNALys3 (red). The primer template duplex (PBS) sits in the HIV RT cleft, positioning the 3’ end of the primer near the active site. The tRNA rearranges to form an extended structure jutting away from RT, and HIV viral RNAs fold near the active site. Structure was solved initially at 8Å global, and 4.2Å core RT-RNA resolution using cryoEM, explaining why initiation is slow due to a mispositioned primer in the RT active site.
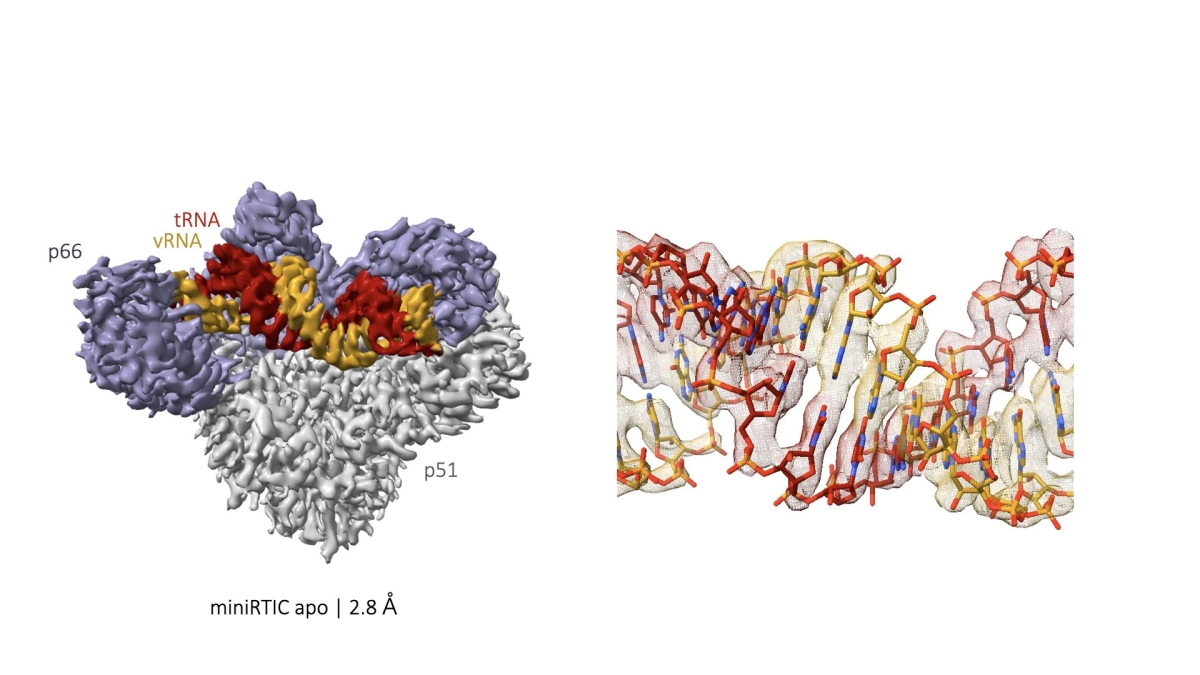
Figure 10
Figure 9 Structure of the core of the HIV-1 RT initiation complex solved to <3Å using cryoEM by trimming peripheral RNA elements. The tRNA-viral RNA complex was modeled de novo using these high-resolution data, which allowed mapping of RNA-protein contacts

Figure 11
Figure 11 High resolution structures of non-nucleoside reverse transcription inhibitors (nnRTs) bound to the HIV-1 RT initiation complex, showing how these drugs bind and inhibit initiation.
